


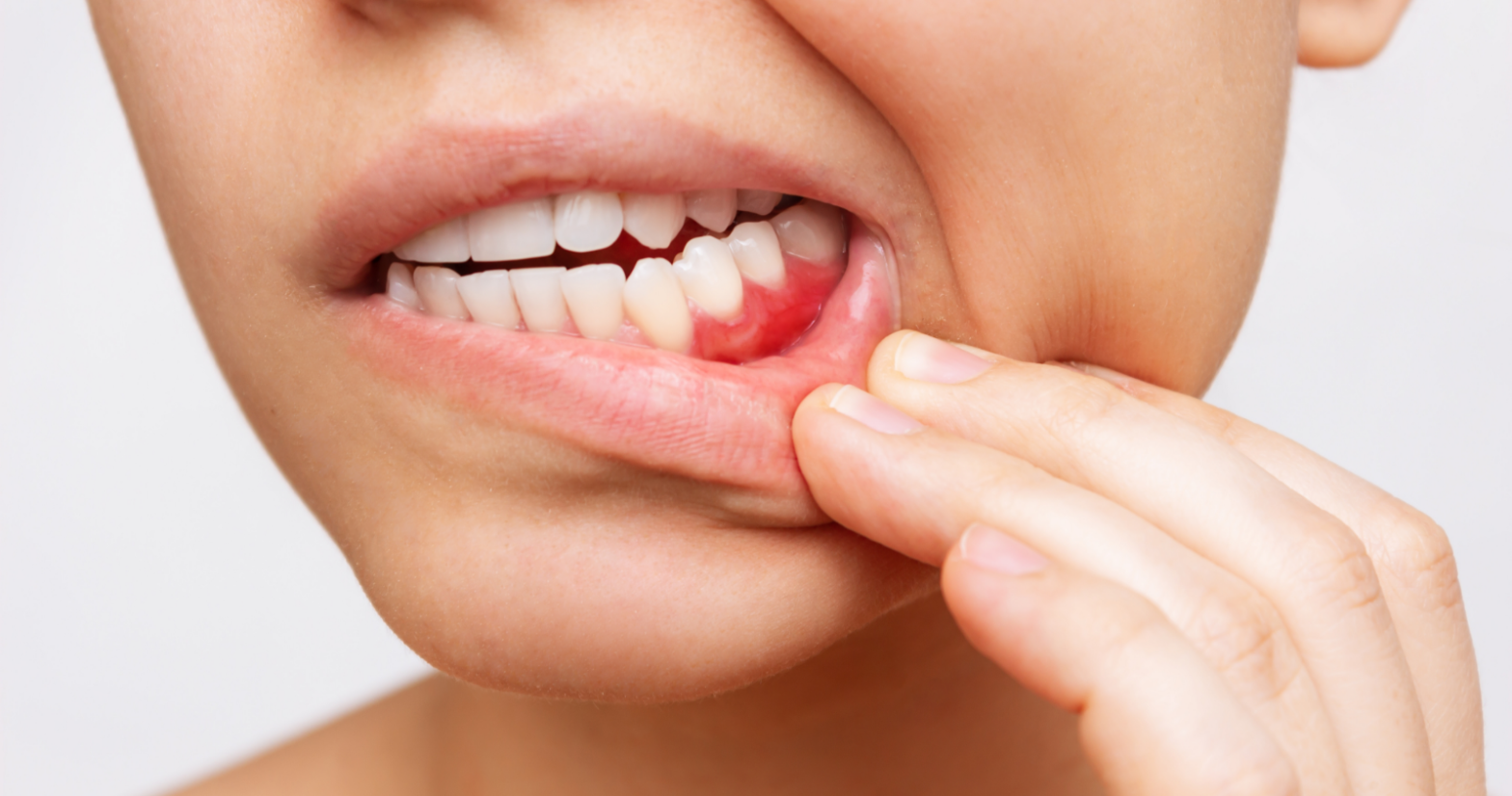
Wearing braces, dentures, crowns, bridges and other orthodontic appliances often irritates and damages the oral mucosa. Small wounds develop on it, which are accompanied by inflammation with swelling, pain and bleeding. Gums can also be injured by dental procedures such as tooth extraction and root cleaning.

Swelling occurs at the site of the gum injury, accompanied by pain and bleeding.
In the first step of wound healing, a network of fibrous proteins is formed in which the platelets get caught. The resulting clot plugs the wound, preventing excessive blood loss.
When Gengigel is applied to the wound, hyaluronic acid from Gengigel gets into the holes in the mesh, where it has an anti-inflammatory effect and reduces swelling. Hyaluronic acid helps the surrounding cells to form collagen, the main component of new tissue. Gengigel forms a thin layer on the surface of the wound that protects the wound from bacteria and other foreign bodies.
In the end, the mesh or clot disappears and the tissue is regenerated.
The wound has healed.
I had dental surgery last week, tooth was removed. A large wound remained, which the doctor sewed up. I then used Gengigel Gel and applied it carefully. The wound healed extremely quickly and there was no inflammation. Great, I recommend it !
Martina P. from St. Gallen
At the moment - after a painful dental treatment - Gengigel is helping me effectively + pain-relieving with oral hygiene + healing!
Cecile S. from Lucerne
I had a serious tooth operation and immediately used Gengigel gel afterwards. The wound healed quickly and there was no inflammation.
Chrigu N. from Winterthur
Clinical studies showed that hyaluronic acid 0.1% / 0.8% (GENGIGEL® Professional) led to a significant improvement in relevant clinical parameters and improved healing in patients with periodontal diseases and in patients undergoing dental surgery. The glycosaminoglycan hyaluronic acid (HA) is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It has many functions, including maintaining tissue homeostasis and protecting […]

Does Diet Affect Gum Health? The results of a study in the "Journal of Clinical Periodontology" suggest this connection. Gingivitis, a common inflammatory disease of the gums, is often the onset of a more destructive disease called periodontitis. When fully developed, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss. Therefore, it is important to […]

Every child knows that brushing your teeth is important, so it is not surprising that most people think of their dental health first when it comes to proper oral hygiene. However, in order to keep our entire set of teeth healthy and functional in the long term, not only is proper dental care and interdental care (interdental care) essential, but also […]

Since general daily oral hygiene focuses mainly on preventing tooth decay, plaque formation and brushing and keeping our teeth clean, unfortunately little attention is usually paid to the gums. Most people have bleeding gums or inflamed gums at some point. As a rule, however, little is done without being aware that this […]

A friendly smile opens doors - privately and professionally, so it is not surprising that more and more people today are not only concerned about the health of their teeth, but also about the aesthetics of them. It is often forgotten that the gums visible when smiling also have a decisive influence on the impression. Beauty and vitality will […]

For many teens, wearing braces can cause temporary mouth sores. These wounds heal much better and faster when using the Gengigel gel or spray. Apply whenever there is a need. Braces serve the purpose of eliminating malpositions of the rows of teeth in the jaw and straightening the rows of teeth. Unfortunately, this also […]

Aphthae are small but quite painful sores in the mouth or on the inner part of the lips. They show a whitish coating and are surrounded by a reddish edge. Medicine speaks of recurring aphthous stomatitis and thus describes one of the most common injuries to the oral mucosa: it affects the buccal mucosa, the mucous membranes on the inner […]

Whitening or in English: bleaching of the teeth is becoming more and more popular and is also increasingly being carried out at home. Home bleaching or do you prefer in-office bleaching? There are numerous products to choose from that you can use at home: from gel-filled splints to strips and pen-shaped applications, it is up to the user to [...]
Bleeding gums or gum swelling can have various causes. If you find blood on the toothbrush or in the mouth after brushing your teeth, it is usually a bacterial infection of the gums or periodontium. The periodontium is the periodontium. If the gums are inflamed and swollen, it is called gingivitis, but if the periodontium […]
Oral health is more important than you might think. The health of your mouth, teeth and gums can affect your overall health - at the same time physical illnesses can affect the health of your mouth. What is the connection between oral health and general health? In your mouth, as in the rest of your body, there is a […]